Fuel your physics prowess with our ‘Class 9 Physics Past Paper Fiesta: 2018 Edition.’
Dive into a tailored treasure trove where key concepts and exam trends unite for an unbeatable prep experience. Unearth crisp answers and vibrant diagrams that make understanding a breeze. Your journey to physics success begins here, where past papers, your guiding star, illuminate the path. Elevate your learning adventure with us!”
Short Answer Questions.
Q1. What Is Plasma Physics?
Plasma Physics:–
Plasma physics, a branch of physics, investigates the behavior of plasmas—ionized gases with charged particles. This field delves into the properties and dynamics of plasmas, commonly observed in stars, lightning, and man-made devices like plasma TVs.
Q2. Define Newton.
Newton:–
The newton (symbol: N) serves as the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). Defined as the force required to accelerate a one-kilogram mass at a rate of one meter per second squared.
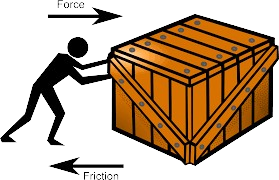
Q3. What do you meant by Friction?
Friction:–
Friction, the force opposing relative motion between surfaces in contact, acts parallel to these surfaces. It can be both advantageous (providing traction) and disadvantageous (causing wear and energy loss).
Q4. Define Weight.
Weight:–
Weight denotes the force exerted on an object due to gravity, calculated as the product of the object’s mass and the acceleration due to gravity.
Q5. Define Variable Velocity.
Variable Velocity:-
Variable velocity characterizes a situation where an object’s speed and/or direction change over time, indicating a non-constant rate of motion.
Q6. What is Vector?
Vector :–
A vector, a quantity with both magnitude and direction, is represented by an arrow. The arrow’s length signifies the magnitude, and its direction indicates orientation.
Q7. Define Stress.
Stress:–
Stress is the force applied per unit area on a material, measuring the material’s internal resistance to deformation.
Q8. What is Principle of Lever?
Principle of Lever:-
The principle of the lever asserts that, for a system in equilibrium, the product of the applied force and the distance from the fulcrum remains constant.
Q9. Power and its Units.
Power and its Units:-
Power, the rate at which work is done or energy transferred, is measured in watts (W) in the International System of Units (SI). One watt equals one joule per second.
Q10. What is Specific Heat?
Specific Heat:–
Specific heat is the amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius, expressed in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/(kg·°C)).
Q11. Define Convection.
Convection:–
Convection, a heat transfer process, involves the movement of a fluid (liquid or gas) due to temperature differences. This process plays a role in phenomena such as boiling water and atmospheric circulation.
Q12. What is Rotatory Motion?
Rotatory Motion:–
Rotatory motion refers to the circular or rotational motion of an object around an axis, exemplified by the rotation of a wheel or the spinning of a top or swing.
Q13. Define Static Friction.
Static Friction:–
Static friction is the frictional force opposing the initiation of motion between two surfaces. It comes into play when an object is at rest and is overcome by an applied force.
Q14. What are Parallel Forces?
Parallel Forces:–
Parallel forces act along parallel lines, though not necessarily in the same direction. The resultant of parallel forces can be determined through vector addition.







