This article is related to Chapter Light of Science Fact File Book 2 for Secondary classes. Through 20 essential definitions and 100 concise Q&A sessions, it offers a comprehensive exploration of topics ranging from reflection to the electromagnetic spectrum. Whether you’re a student or an enthusiast, this provides invaluable insights into the fundamental nature of light.
Few important definitions from Chapter Light:
Few important definitions from Chapter Light are as follows:
-
Light:
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye and enables us to perceive color, shape, and depth in our surroundings.
-
Luminous objects:
Luminous objects are those that emit light of their own, such as the Sun, stars, or light bulbs.
-
Non-luminous objects:
Non-luminous objects do not emit light on their own but can be seen by reflecting light from a luminous source. Examples include the Moon, planets, and most everyday objects.
-
Opaque:
Opaque materials do not allow light to pass through them, preventing the transmission of light. These materials completely absorb or reflect light, making objects behind them invisible.
-
Transparent:
Transparent materials allow light to pass through them easily, enabling objects on the other side to be clearly visible. Examples include glass and clear plastic.
-
Translucent:
Translucent materials allow some light to pass through them but scatter or diffuse the light, making objects on the other side appear blurred or obscured. Examples include frosted glass and wax paper.
-
Diffraction:
Diffraction is the bending of light waves around obstacles or through openings, causing them to spread out and produce patterns of light and dark fringes.
-
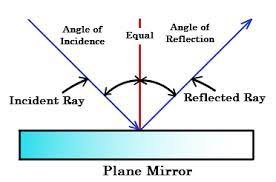
Reflection:
Reflection occurs when light waves bounce off a surface, such as a mirror, and change direction. This phenomenon allows us to see objects by the light they reflect.
-
Refraction:
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, such as from air to water or from air to glass. This bending causes the direction of light to change, leading to phenomena like the bending of a pencil in water.
-
Pigments:
Pigments are substances that selectively absorb and reflect certain wavelengths of light, giving objects their color. Common pigments include those found in paints, inks, and dyes.
-
Spectrum:
The spectrum refers to the range of colors produced when white light is dispersed, typically seen as a continuum of colors from red to violet, as in a rainbow or when light passes through a prism.
-
Dispersion:
Dispersion is the separation of white light into its component colors as it passes through a medium like a prism, due to each color having a different wavelength and thus bending at different angles.
-
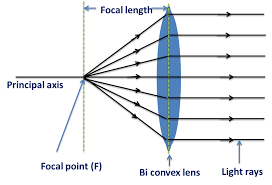
Convex lens:
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than at the edges and converge light rays, causing them to come together at a focal point. It can form real or virtual images depending on the object distance.
-
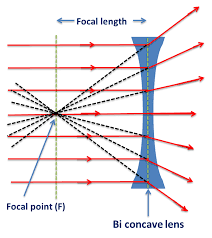
Concave lens:
A concave lens is thinner in the middle than at the edges and diverge light rays, causing them to spread out. It forms only virtual images and cannot project real images.
-
Prism:
A prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract and disperse light, separating it into its component colors. It’s often used in experiments or to create rainbows.
-
Mirage:
A mirage is an optical illusion caused by atmospheric refraction, where light bends due to temperature gradients, creating false images of distant objects, such as water appearing on a hot road.
-
Apparent depth:
Apparent depth is the perceived depth of an object or image as seen through a refractive medium, such as water or glass, which can make objects appear closer or farther than they actually are.
-
Real depth:
Real depth is the actual distance or depth of an object, unaffected by the medium through which it is viewed, such as in air or vacuum.
-
Rainbow:
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon caused by the dispersion, refraction, and reflection of sunlight in water droplets, resulting in a spectrum of colors appearing in the sky.
-
Plane Mirror:
A plane mirror is a flat, smooth surface that reflects light rays without distorting them. It forms virtual images that are laterally inverted but maintain the same size and distance as the object being reflected. These mirrors are commonly used in everyday applications such as mirrors in bathrooms, dressing rooms, and periscopes.
Quizzes related to Chapter Light:
Solve these quizzes to learn more about this topic.
You can also download the pdf of all these objectives.
You can also download the pdf of all these questions and answers.








78 comments