Short Question Answers.
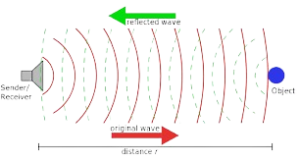
Q1. What is ultrasonic?
Ans. Ultrasonic:
Ultrasonic refers to sound frequencies beyond the upper limit of human hearing, typically above 20,000 hertz. It finds applications in medical imaging, cleaning, and industrial testing.
Q2. Define kilowatt-hour.
Ans. Kilowatt-Hour:
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of electrical energy equivalent to one kilowatt of power used for one hour. It is commonly used to measure electricity consumption.
Q3. What is DC motor?
Ans. DC Motor:
A DC motor is an electric motor that runs on direct current (DC) and converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It operates based on the interaction of magnetic fields, causing rotation.

Q4. Define stable nuclides.
Ans. Stable Nuclides:
Stable nuclides are atomic nuclei that do not undergo radioactive decay. They remain unchanged over time and are not subject to spontaneous disintegration.
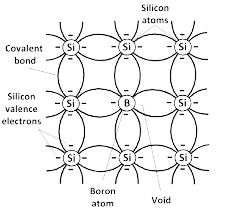
Q5. What is p-type semiconductors?
Ans. P-type Semiconductors:
P-type semiconductors have positive charge carriers (holes) as the majority charge carriers. They are created by adding certain impurities to pure semiconductors.
Q6. What is remote control?
Ans. Remote Control:
A remote control is a device that wirelessly operates electronic devices, such as TVs or appliances, from a distance. It uses infrared signals or radio waves for communication.
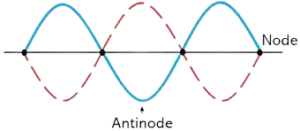
Q7. Define antinode
Ans. Antinode:
An antinode is a point of maximum amplitude in a standing wave where constructive interference occurs. In such regions, the amplitudes of the individual waves reinforce each other.
Q8. Why cannot sound travel in a vacuum?
Ans. Sound in a Vacuum:
Sound requires a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) for transmission. In a vacuum, there is no medium, so sound waves cannot propagate.
Q9. State the left-hand rule
Ans. Left-Hand Rule:
The left-hand rule is a mnemonic and conceptual tool used in electromagnetism to establish the relationships between the direction of magnetic fields (index finger), electric currents (middle finger), and the resulting force on a conductor (thumb). This rule aids in quickly determining the orientation of these elements in different physical situations, providing a visual and memorable guide in the study of electromagnetic phenomena.
Q10. Write two uses of concave mirror
Ans. Uses of Concave Mirror:
Concave mirrors are used in makeup mirrors to provide magnification.
They are used in headlights of automobiles to focus light from the bulb.
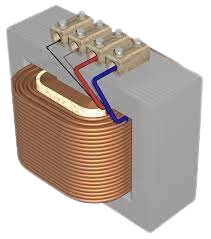
Q11. What is step-up transformer?
Ans. Step-Up Transformer:
A step-up transformer increases the voltage while decreasing the current. It has more turns in the secondary coil than in the primary, used in power distribution.
Q12. Write down two precautions to minimize radiation dangers
Ans. Precautions to Minimize Radiation Dangers:
1. Use shielding materials to reduce exposure.
2. Minimize time spent near radiation sources.
3. Increase distance from radiation-emitting objects.







