Embark on a journey of academic excellence with the introduction of our meticulously crafted resource, “Physics Notes of Past Paper for Class 10.” Tailored for the specific needs of students in the year 2019, these notes function as your compass for navigating the intricacies of the physics curriculum, providing a comprehensive review of essential concepts and exam trends.
Let’s delve into the world of physics, equipped with insights gained from past papers.
Ensure thorough and effective preparation for success with these notes.
Short Question Answers.
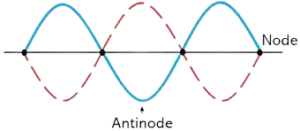
Q1. Define Stationary waves.
Ans. Stationary Waves:
Stationary waves are patterns of vibration that result from the interference of two waves with the same frequency and amplitude traveling in opposite directions. Nodes and antinodes characterize them.
Q2. What is Audible frequency ranges?
Ans. Audible Frequency Range:
Audible frequency ranges refer to the frequencies of sound waves that the human ear can detect. Typically, this range spans from about 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
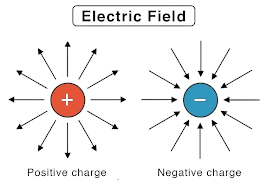
Q3. What is Electric field?
Ans. Electric Field:
An electric field is a region surrounding a charged object where another charged object experiences a force. It is a vector quantity, and its strength is measured in volts per meter.
Q4. Define Conventional current.
Ans. Conventional Current:
Conventional current is the flow of positive charge. Despite electrons being the actual carriers of charge in most materials, conventional current assumes positive charges moving in the opposite direction.
Q5. What do you mean by Power of Lens?
Ans. Power of a Lens:
The power of a lens is a measure of its ability to converge or diverge light. It is measured in diopters (D) and is the reciprocal of the focal length in meters.
Q6. Define short sightedness.
Ans. Short Sightedness:
Short-sightedness, or myopia, is a vision condition where distant objects appear blurry. This occurs when light entering the eye focuses in front of the retina instead of directly on it.
Q7. What is meant by Radioisotopes?
Ans. Radioisotopes:
Radioisotopes are isotopes of an element that exhibit radioactivity. They are used in various fields, including medicine (for imaging and treatment) and industry (for testing and measuring).
Q8. What is meant by Infrasonic?
Ans. Infrasonic:
Infrasonic refers to sound frequencies below the range of human hearing, typically below 20 Hz. Examples include seismic waves and certain animal communications.
Q9. What is the main difference between telephone and cellular phones?
Ans. Difference between Telephone and Cellular Phones:
Telephones are wired communication devices, whereas cellular phones use wireless technology. Cellular phones provide mobility and use a network of cell towers for communication.
Q10. If mass = 20 kg and c = 3×10^8 meter per second then find the value of E.
Value of E (Energy):
Formula: E = m x c^2
m = 20kg
c = 3 x 10^8 m/s
E = 20 x (3 x 10^8)2 = 1.8 x 10^18 J
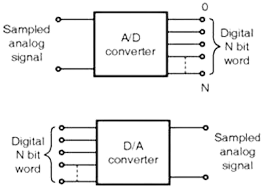
Q11. What is meant by ADC and DAC?
Ans. ADC and DAC:
ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) converts analog signals to digital, and DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter) converts digital signals back to analog. They are crucial in digital communication and signal processing.
Q12. Define Ohm’s law.
Ans. Ohm’s Law:
Ohm’s Law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, given a constant temperature. It is expressed as V = IR.
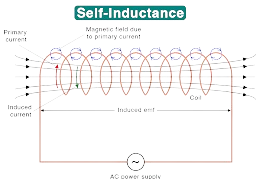
Q13. What do you know about Self-induction?
Ans. Self-Induction:
Self-induction occurs when a changing current in a coil induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the same coil, opposing the change in current.
Q14. What is meant by Real depth and Apparent depth?
Real Depth and Apparent Depth:
Real depth is the actual distance between objects underwater. Apparent depth is the depth perceived by an observer and can be affected by the refraction of light.
Q15. If C = 5 micro Farad and V = 2 volts, then find the value of Q.
Ans.
Value of Q (Charge):
Formula Q = CV,
Here C = 5 x 10^-6 F
V = 2 volts
Q = 5 x 10^-6 x 2 = 0.00001 Coulombs.
In conclusion, as you navigate the path towards achieving proficiency in Class 10 Physics, consider our “Physics Past Paper for Class 10” as a guiding beacon and a rich reservoir of knowledge. These notes, armed with a profound understanding of crucial concepts and aligned with exam trends, serve as the key to unlocking success in the upcoming examinations. Seize the opportunity to maximize this comprehensive resource and advance confidently into the realm of physics, equipped with insights derived from past papers. May your academic journey be enriched, and may your achievements in Class 10 Physics reach stellar heights.







