Prepare for 10th Class Physics achievement with our exclusive ‘Physics Past Paper Notes.’
Crafted for the year 2021, these notes encompass vital concepts and examination patterns, establishing them as your primary resource for thorough preparation. Here, you will find concise answers to the questions given in the paper along with diagrams that aid in a clearer understanding.
Short Question Answers.
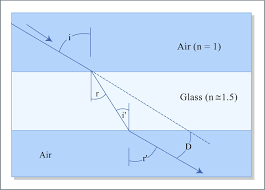
Q1. Define Refraction.
Ans. Refraction:
Refraction is the bending of a wave, such as light or sound, as it passes from one medium to another with a different optical density. This bending is caused by a change in the wave’s speed.
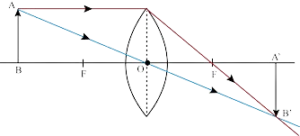
Q2. Define Linear Magnification.
Ans. Linear Magnification:
Linear Magnification is the ratio of the height of an image to the height of the object in linear terms. It is commonly used in optics to describe the size of images formed by lenses or mirrors.
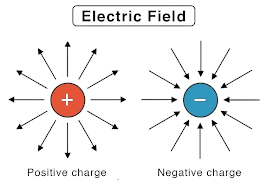
Q3. What is Electric field?
Ans. Electric Field:
An electric field is a region in which an electric charge experiences a force. It is created by a charged object and is characterized by the force that a positive test charge would experience at any point in the field.
Q4. Define Voltmeter.
Ans. Voltmeter:
A voltmeter is an instrument used to measure the potential difference (voltage) between two points in an electrical circuit. It is connected in parallel to the component or circuit being measured.

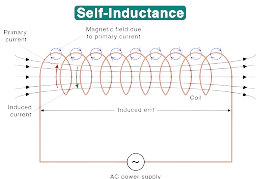
Q5. Define the term Self-induction.
Ans. Self-Induction:
Self-induction is the phenomenon in which a changing current in a coil induces an Electromotive force (EMF) in the same coil. It is a form of inductance that opposes changes in current.
Q6 .Write two properties of gamma rays.
Ans. Properties of Gamma Rays:
- Gamma rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation.
- They have high energy and penetrating ability, making them useful in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
Q7. What is Semiconductor?
Ans. Semiconductor:
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Commonly used in electronic devices, semiconductors include silicon and germanium.
Q8. What is Spring constant?
Ans. Spring Constant:
The spring constant is a measure of the stiffness of a spring. It relates the force exerted by a spring to the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position. It is denoted by ‘k’ in Hooke’s Law.
Q9. Define Joule’s law.
Ans. Joule’s Law:
Joule’s Law states that the heat produced in a resistor is proportional to the square of the current passing through it, the resistance, and the time for which the current flows.
Q10. Write causes of energy in sun.
Ans. Causes of Energy in the Sun:
The primary source of energy in the sun is nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium, releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the process.
Q11. Define Analog electronics.
Ans. Analog Electronics:
Analog electronics deals with continuous signals, typically represented by voltages or currents. It contrasts with digital electronics, which uses discrete signals represented by binary code.
Q12. What are Electric lines of force.
Ans. Electric Lines of Force:
Electric lines of force represent the direction and strength of an electric field. They provide a visual way to understand the field’s influence on charged particles.
Q13. Define Simple Harmonic Motion.
Ans. Simple Harmonic Motion:
Simple Harmonic Motion is a type of periodic motion where a restoring force proportional to the displacement acts on an object, resulting in an oscillatory or back-and-forth motion.
Q14. What are Compressional waves?
Ans. Compressional Waves:
Compressional waves, also known as longitudinal waves, are waves in which the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of the wave’s propagation. Sound waves are an example of compressional waves.







