“Prepare for physics excellence with our specialized ‘Class 10 Physics Notes.’
Customized for the 2023 curriculum, these notes comprehensively address essential concepts and exam patterns, establishing themselves as your primary resource for thorough preparation. Within, discover succinct responses to paper questions, accompanied by diagrams enhancing your comprehension.”
Short Question Answer:-
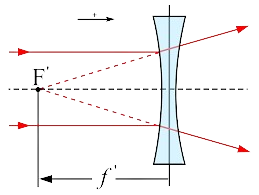
Q1. What is Focal length of a lens?
Ans. Focal Length of a Lens:
Focal length is the distance between the lens’s optical center and its focal point. For converging lenses, it is positive; for diverging lenses, it is negative.
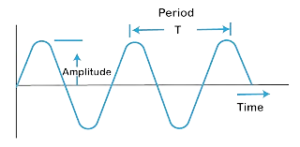
Q2. Define Time period.
Ans. Time Period:
Time period is the duration for one complete cycle of a periodic motion, such as the time taken for a pendulum to swing back and forth.
Q3. How will you charge Polythene rod negatively?
Ans. Charging Polythene Rod Negatively:
Rubbing polythene with a suitable material (like wool) transfers electrons, giving the polythene a negative charge.

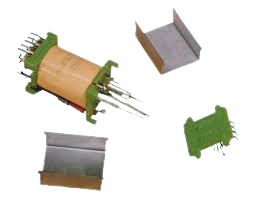
Q4. Define Relay and its work.
Ans. Relay and its Work:
A relay is an electromechanical switch. It works by using an electromagnetic coil to control the opening or closing of a switch in an electric circuit.
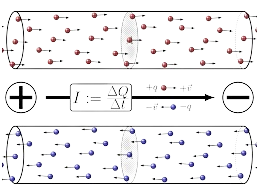
Q5. Define Electric Current.
Ans. Electric Current:
Electric current is the flow of electric charge in a conductor, measured in amperes (A). It is the rate of flow of charge.
Q6. Draw symbol for AND gate and write its truth table.
Ans. AND Gate Symbol and Truth Table:
Symbol:
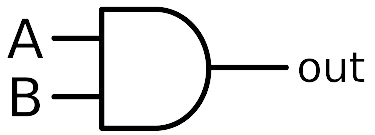
Truth Table:
| A | B | Out |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Q7. Define Half Life.
Ans. Half Life:
The half-life of a radioactive substance is the time required for half of the radioactive nuclei in a sample to undergo decay. It is a measure of the stability of the substance and is characteristic of each radioactive isotope.

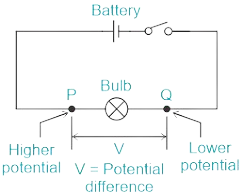
Q8. Define Potential Difference.
Ans. Potential Difference:
Potential difference is the voltage between two points in an electric circuit. It is the driving force for electric current.
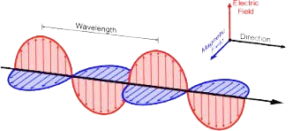
Q9. Define Electromagnetic Waves.
Ans. Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Examples include radio waves, microwaves, and light.
Q10. Define Radius of Curvature and Pole.
Ans. Radius of Curvature and Pole:
In optics, the radius of curvature is the distance from the center of a lens or mirror to its focal point. The pole is the central point on the optical axis.
Q11. Define Quality of Sound.
Ans. Quality of Sound:
The quality of sound refers to its timbre or tone color, which is determined by the relative strengths of the sound’s harmonics.
Q12. Define Electrostatic.
Ans. Electrostatic:
Electrostatics is the study of stationary electric charges and their behavior.
Q13. Define Transformer.
Ans. Transformer:
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction.
Q14. Define Information.
Ans. Information:
Information is data that is organized, meaningful, and useful. It provides knowledge and context.
Q15. Define Digital Electronics.
Ans. Digital Electronics:
Digital electronics involve circuits and systems that use discrete voltage levels to represent information (binary code). It contrasts with analog electronics, which use continuous signals.

In conclusion, as you embark on your journey to master Class 10 Physics, our “Class 10 Physics Notes” emerge as a guiding light and a reservoir of invaluable knowledge. With a profound grasp of essential concepts and a synchronization with prevailing exam patterns, these notes serve as your indispensable tool for conquering success in the impending examinations. Harness the full potential of this extensive resource and stride forward with confidence into the intricate realm of physics, equipped with the insights gleaned from meticulously crafted notes. May your academic voyage be enriched, and may your accomplishments in Class 10 Physics be truly exceptional.







