Get ready for physics excellence with our specialized ‘Class 9 Physics Notes.’
Tailored for the 2023 curriculum, these notes comprehensively tackle essential concepts and exam patterns, establishing themselves as your primary resource for thorough preparation. As you delve into the material, discover succinct responses to paper questions, accompanied by diagrams designed to enhance your comprehension.
Short Answer Questions
(a) Define Pressure and write its units.
Answer. Pressure is the force applied per unit area. The units of pressure are typically measured in pascals (Pa) in the International System of Units (SI), where ‘1’ Pascal equals ‘1’ Newton per square meter (N/m²).
Other common units include atmospheres (atm.) and millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
(b) What are the lower and upper fixed points for a thermometer.
Answer. The lower fixed point of a thermometer indicates the temperature of a specific substance under defined conditions, such as the freezing point of pure ice.
In contrast, the upper fixed point represents the temperature of a fixed substance under specific conditions, like the boiling point of pure water. These fixed points collaboratively establish the temperature scale for the thermometer.
(c) Write two uses of insulators.
Answer. Two Uses of Insulators:
Two use of Insulators are as follows:
-
Thermal Insulation: Buildings use insulators, such as fiberglass or foam, to reduce heat transfer, maintaining a comfortable temperature inside. These materials minimize heat loss in cold weather and heat gain in hot weather.
-
Electrical Insulation: Materials like rubber or plastic serve as electrical insulators, preventing the flow of electric current. These materials are crucial for insulating wires and cables, ensuring the safety of electrical systems and preventing electrical shocks.
(d) What is Plasma Physics.
Answer. Plasma physics, a branch of physics, is dedicated to the study of the behavior of ionized gases or plasmas. Comprising charged particles like ions and electrons, plasma exhibits distinctive electromagnetic properties. This field delves into the foundational principles that govern plasmas, exploring their interactions with electromagnetic fields, and investigates their applications across diverse domains, including astrophysics, fusion research, and technology development.

(e) Define Velocity.
Answer. Velocity is a vector quantity that describes the rate of change of an object’s position with respect to time. It includes both the object’s speed and the direction in which it is moving.
The standard unit of velocity is meters per second (m/s) in the International System of Units (SI).
(f) Define Centre of Mass.
Answer. The center of mass of a system of particles or an object is the point at which the entire mass of the system can be considered to be concentrated. It is the average position of all the mass in the system, taking into account both the mass and the spatial distribution.
In a uniform gravitational field, the center of mass is also the point where gravitational forces can be considered to act on the system.

(g) What is Gravitational Constant?
Answer. The gravitational constant, denoted by “G “, is a fundamental physical constant that appears in Newton’s law of universal gravitation. It is used to quantify the strength of the gravitational force between two objects with masses.
In the formula F = G m1 m2 / r2, where F is the gravitational force, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, and “r” is the separation between their centers, “G” is the gravitational constant. Its approximate value is 6.674 x 10 -11 N. m2 / kg2 in the International System of Units (SI).
(h) Define Mechanical Energy.
Answer. Mechanical energy constitutes the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy within a system. Potential energy is the energy inherent to an object based on its position or state, whereas kinetic energy is the energy linked to its motion.
(i) Define Young Modulus.
Answer. Young’s Modulus, alternatively known as the elastic modulus or modulus of elasticity, measures the stiffness of a material. It quantifies how much a material deforms under an applied force.
Specifically, one defines Young’s Modulus as the ratio of stress to strain within the elastic limit of a material.
Mathematically, it is expressed as:
Young’s Modulus “Y” = Stress / Strain.
The unit of Young’s Modulus in the International System of Units (SI) is Pascal (Pa) or Newton per square meter (N/m²).
(j) Differentiate between Heat and Temperature.
Answer. Difference between Heat and Temperature:-
Temperature:
(k) Two uses of Conductor.
Answer. Two uses of Conductor:
1. Electrical Conductivity:
Conductors, such as copper and aluminum, are used in electrical wiring to transmit electrical current. Their high conductivity allows for efficient and low-resistance flow of electricity, making them essential in power distribution systems and electronic devices.
2. Thermal Conductivity:
Conductors are employed in heat transfer applications. Materials with good thermal conductivity, like metals, are used in heat exchangers, cooking utensils, and other devices where the efficient transfer of heat is necessary.
(l) Define Moment Arm.
Answer. The moment arm, alternatively referred to as the lever arm or torque arm, represents the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of a force. It plays a crucial role in determining the torque (rotational force) exerted by a force on an object.
The longer the moment arm, the greater the torque produced by a given force. Mathematically, torque T is calculated as the product of the force “F” and the moment arm “r”:
T = F . r
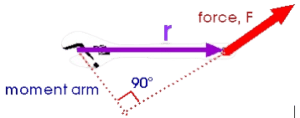
The unit of the moment arm is typically measured in meters (m).
(m) Define Newton’s Second law of Motion.
Answer. Newton’s Second Law of Motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
where:
- “F” is the net force acting on the object,
- “m” is the mass of the object,
- “a” is the acceleration produced by the net force.
This law explains how the motion of an object changes when subjected to an external force. Furthermore, it is a fundamental principle in classical mechanics and a key equation for understanding and predicting the dynamics of objects.
(n) Name any four measuring instruments.
Answer. Measuring instruments.
1. Ruler or Tape Measure:
A measuring ruler or tape is used for measuring linear dimensions, such as length or height.
2. Thermometer:
A thermometer is a device that measures temperature.
3. Voltmeter:
A voltmeter is a device that measures electrical voltage.

4. Spectrophotometer:
A spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light at different wavelengths, and it is commonly employed in chemistry and biology for the analysis of substances.







